The Middle East Energy Development Company has implemented two national crude oil desalination projects for the clients of the southern oil-rich regions as follows:
- Project of conducting preliminary and detailed engineering studies and preparation of PC tender documents to create the required facilities for oil and gas processing of Maroon Asmari – 3 (1225-71-53)
- Project of conducting preliminary and detailed engineering studies and preparation of PC tender documents to create the required facilities for oil and gas processing of Maroon Asmari – 5 (1225-71-53)
Also, conducting numerous studies and experiments in the field of sweetening of crude oil in its research center has valuable experiences in carrying out these projects.
Maroon field is one of the major oil fields in the south of the country, which is located in the Maroon region of Khuzestan (about 60 km east of Ahvaz) and is located and produced from Asmari and Bangestan formations. The oil of this reservoir is currently separated from the associated gases after extraction in the existing facilities and sent to the oil consumption or export centers. The first production started in 1969. The Asmari Formation was operated as a natural discharge until 1989, until that time gas injection was started to maintain reservoir pressure and increase the recovery factor. By drilling new wells and repairing wells that have problems with excess gas or water production, efforts have been made to prevent a drop in production. In recent years, despite the fact that the oil of the Asmari Formation has been free of H2S gas, the oil produced is impregnated with this gas, which has caused several problems.
Produced oil up to 15% (on average) can contain water, but the amount of salt leaving the field for export or domestic refineries should not be respectively more than 43 and 29 grams per cubic meter. Water was injected along with the production in Aghajari Formation, but this work was stopped due to water leakage to the surface. Facility issues include limited capacity and inefficient performance of desalination units, processing and injection of reservoir water due to environmental issues and reservoir oil acidification.
So far, several arrangements have been made by the operator and the client for the problems of this field, the most important of which are the limited capacity and inadequate efficiency of desalination units, processing and injection of reservoir water due to environmental issues and acidification of reservoir oil. Occurrence of the problem of acidification of Asmari reservoir oil in recent years, investigation and solution of this phenomenon requires measures taken by the esteemed client in the form of a project to optimize the Maroon field processing system, a project entitled Preliminary engineering studies, basic design, detailed design and also preparation PC project bidding documents were defined to provide the required facilities for Marun Asmari oil and gas refining.
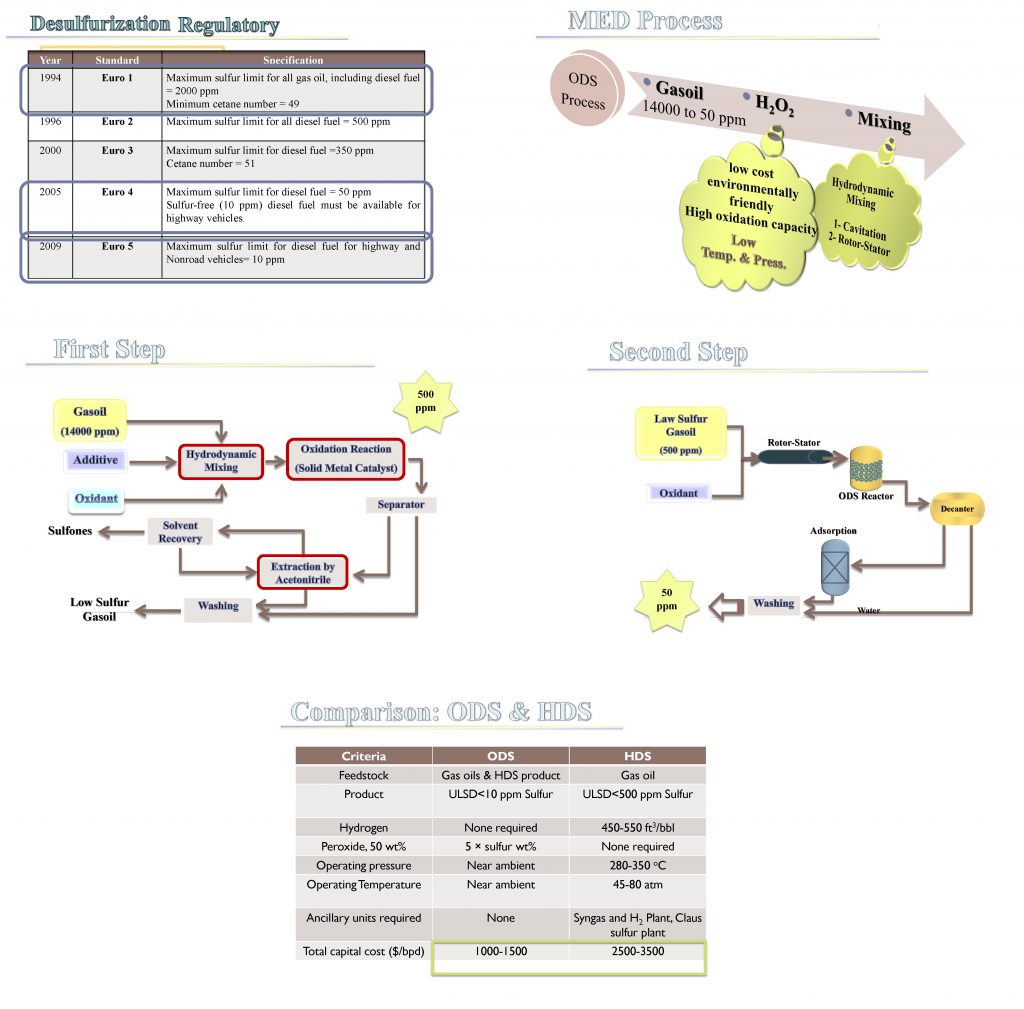
Crude oil produced from the country’s oil fields contains associated gas, which is usually separated in 4 stages of pressure relief separation vessels located in the exploitation units (PU). The pressure is the last stage of atmospheric separation, as a result of which the RVP (REID Vapor Pressure) stabilizes the crude oil output from the PU at the appropriate level.
Also, due to the increase in water in most of the crude oil produced, the amount of salt has exceeded the allowable limit, and the crude oil stabilized in the exploitation units is desalinated in another unit. Also, crude oil produced from most of the country’s oil fields contains hydrogen sulfide (H2S), part of which is separated by gas along with the separation vessels and the other part remains in crude oil. According to the client’s request, the amount of H2S accepted in crude oil, the goal of the National Company of Southern Oilfields is to reduce the H2S of crude oil in this unit to the level of 15 PPM.
Hydrogen sulfide is a volatile substance whose volatility or fugacity is mediated by the volatility of ethane and propane. The crude oil solution is separated from the crude oil by light gases. However, in many cases, the amount of hydrogen sulfide remaining in the crude oil is too much and therefore the use of separation vessels in several stages is not able to reduce the amount of hydrogen sulfide to the desired level and the use of other advanced techniques is necessary.
There are various physical and chemical methods to eliminate or reduce H2S in crude oil or hydrocarbon fluids, some of which are in the testing or pilot phase. But the usual method, proven and working to reduce H2S crude oil at the international level, especially in Iran is the method of stripping by sweet gas.
The process of stripping and stripping installation in operation units is technically and economically important in order to reduce H2S in different places, oil vapor pressure stabilization and desalination. In this regard, the following factors have been considered in option optimization.
– Ease of operation in achieving H2S level and need for heater (Reboiler), heat exchanger, cooling pump and cooler
– Investment in required facilities
– The amount of sweet gas for stripping as well as fuel gas
– Crude oil vapor pressure (RVP)
– Initial investment cost and annual operations
– Site required and available to install sweetening facilities
– Ease of implementation of sweetening project with minimal reduction of capacity or stopping the operation unit
– The quality of sweetened crude oil in terms of API Gravity
– The amount or volume of sweetened crude oil
-Problems with accessing the required sweet gas and reusing it
The common method for reducing the amount of H2S in crude oil is stripping in both hot and cold states.
Investigation of H2S removal methods
According to the studies performed in connection with H2S removal methods, the following methods can be mentioned:
- Using Conventional Stripper (Cold Stripping)
- Using Reboiled Stripper (Hot Stripping):
Using preheater (pre heater)
Using the tower, along with the Reboiler
Using the tower, along with (Distilation) Reflux, Rrboiler
- Using chemical methods
This method is often done by sulfur oxidation, which uses the following materials to de-H2S:
1- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
2- Ammonia (NH3)
3- Amen